Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
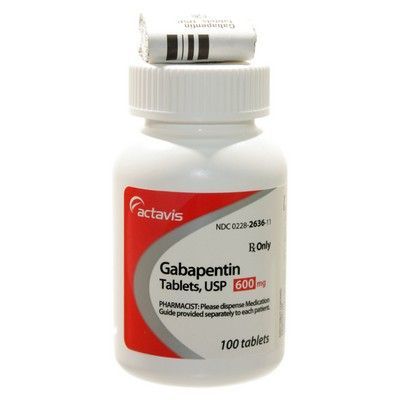
Gabapentin is a widely used anticonvulsant and nerve pain medication that has attracted some controversy. But why would a dentist even prescribe gabapentin—and why should you know if your dental patients are taking it? Additionally, gabapentin is utilized in the management of restless leg syndrome and various forms of neuropathic pain, such as diabetic neuropathy.It is important to note that gabapentin is a prescription medication and should only be used for the specific conditions it is prescribed for. “We hypothesized that using a combination of the non-opioid pain medications and adding gabapentin to the mix for pain would be an effective strategy to minimize or eliminate opioids for dental pain,” said Yanfang Ren, DDS, PhD, MPH, professor and clinical chief, Howitt Urgent Dental Care. The Role of Gabapentin in Managing Tooth Pain. Gabapentin, a medication originally developed to treat epilepsy, has gained recognition for its effectiveness in managing nerve-related pain, including toothaches. This medication works by modulating the activity of certain neurotransmitters in the brain, reducing the transmission of pain signals. A combination of analgesics prescribed with gabapentin after dental procedures was shown to be just as effective for treating pain as opioids, researchers reported in JAMA Network Open. Also most tooth pain is caused by nerve pain, there for gabapentin will most definitely help! Just do not take to many because you can become dizzy, loopy, and tired. I hope anyone with tooth pain and access to gabapentin does not read and listen to the people who said that it will not help! Thank you have a great day! Compared with 2012, when opioid combinations or ibuprofen alone were predominant, acetaminophen, ibuprofen, acetaminophen/ibuprofen, and gabapentin in a multimodal strategy were used more frequently in 2022. No opioids were prescribed for dental pain from Mach 2021 to February 2022. These studies suggest gabapentin can be effective in controlling pain, including tooth pain, as it is more effective than a placebo and other pain medications in some cases. Pre-emptive gabapentin (GBP) and pregabalin (PGB) have been extensively used in the medical field to control postoperative pain . The idea of preemptive analgesia is to administer medications before the initiation of a pain stimulus or before the process of central sensitization. In Miami, tooth decay is a significant public health issue, partly fueled by excessive sugar consumption. Gabapentin, primarily used to treat nerve pain, surprisingly also affects oral health. Some studies suggest its use may exacerbate tooth decay. This highlights the need for more research on Gabapentin's role in dental health. The best pain reliever for a tooth ache, or really any transient pain is ibuprofen. (I worked with a dentist for 15 years.) If you don't already take Gabapentin, no one is going to prescribe it for you for a tooth ache. These studies suggest gabapentin can help with tooth pain, as it is effective in controlling pain and provides substantial relief for chronic neuropathic pain conditions. Dentists frequently prescribe opioids for dental pain and contribute substantially to new and persistent opioid use. 1 Although the American Dental Association recommends nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for managing pain, 2 opioids continue to be used more than nonopioids. 3 This may partly be explained by the lack of alternatives to opioids, especially when NSAIDs or Many people wonder how much gabapentin is necessary for tooth pain, especially when traditional over-the-counter medications don’t provide relief. This article explores the ins and outs of gabapentin, its effectiveness in treating tooth pain, recommended dosages, potential side effects, and considerations to keep in mind. Known as an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat epilepsy and nerve pain, gabapentin has been gaining popularity as a remedy for wisdom tooth pain. In this article, we will explore whether gabapentin is truly effective in alleviating the agony caused by emerging wisdom teeth. Gabapentin, in combination with other analgesics, can help manage toothache pain. Gabapentin, an anticonvulsant drug, has been found to be beneficial in managing dental pain, particularly when used in combination with other analgesics. Here are some of the benefits of using gabapentin for dental pain: Buprenorphine (0.005–0.02 mg/kg) is considered a partial mu agonist (i.e., it only partially stimulates the receptor), making it less effective than the pure mu agonists, and is used for mild to moderate pain. This drug is used more commonly for cats to avoid the adverse effects of pure mu agonists. Gabapentin is a medication commonly used to treat nerve pain, including tooth pain. It works by binding to calcium channels in the brain and spinal cord, which helps to reduce the release of certain neurotransmitters involved in transmitting pain signals. In a new study at the University of Rochester Medical Center’s Eastman Institute for Oral Health (EIOH), researchers found that gabapentin, when combined with ibuprofen or acetaminophen, was more effective than opioids in relieving pain after tooth extractions.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |