Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
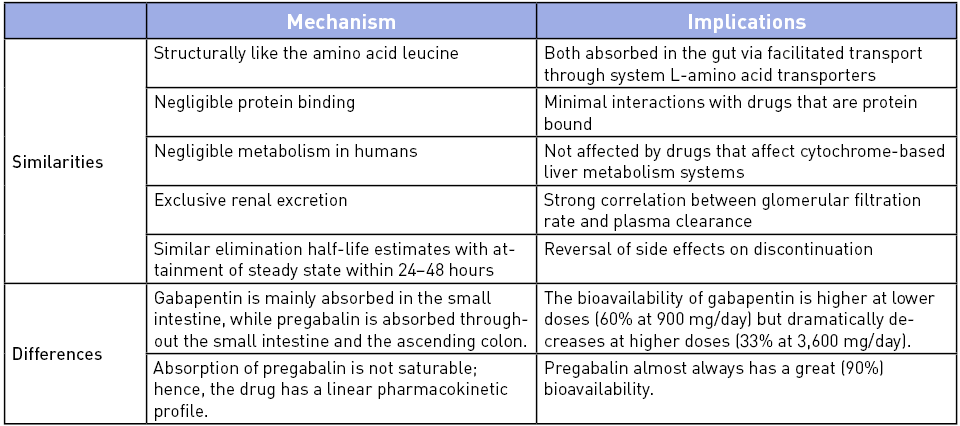
Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly prescribed as first-line treatments for postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) in China due to their safety profile in therapeutic doses [16, 17]. The previously proposed mechanism of action, which involves a selective inhibitory effect on voltage-gated calcium channels containing the α2δ-1 subunit, has been Recent meta-analyses comparing gabapentin and pregabalin in the treatment of various neuropathic pain conditions have shown superior pain control with pregabalin. A Cochrane review from 2015 demonstrated a comparable number needed to treat (NNT) for a 50% reduction in pain intensity for both medications, independent of the etiology of pain. Keywords: Cost-effectiveness, Gabapentin, Peripheral neuropathic pain (pNeP), Postherpetic neuralgia (PHN), Pregabalin Introduction Peripheral neuropathic pain (pNeP) is a general pain disorder caused by a lesion or disease of the peripheral somatosensory nervous system and occurs frequently with diabetes or following herpes zoster reactivation. Pregabalin is licensed for peripheral and central neuropathic pain whereas gabapentin is licensed for peripheral neuropathic pain only. Use of gabapentin for central neuropathic pain is therefore off-label. Pregabalin is the newest agent to gain approval for PHN. Data suggest efficacy for relief of pain and sleep disturbance secondary to PHN in affected patients. Although there are no head-to-head comparisons, pregabalin appears comparable to gabapentin and other first-line agents for treating PHN. Gabapentin (GPT) and pregabalin (PGB) are two commonly used drugs for the treatment of PHN, but there have been broad concerns regarding their efficacy and safety. Thus, this retrospective cohort study was conducted to investigate the effectiveness and safety of GPT versus PGB in the treatment of PHN. By substituting gabapentin with pregabalin in postherpetic neuralgia therapy, we can compare the two drugs. Methods: In 32 PHN patients being administered gabapentin, without changing the frequency of dosing, the drug was substituted with pregabalin at one-sixth dosage of gabapentin. Pregabalin appears to have a better overall therapeutic effect than gabapentin for patients with PHN, but gabapentin has a lower incidence of adverse reactions and a better safety profile. Clinicians should comprehensively consider patient factors and fully evaluate the advantages and disadvantages Although both gabapentin and pregabalin are first-line drugs for neuropathic pain including postherpetic neuralgia (PHN), no report has directly compared the magnitude of pain relief and the incidence of side effects of both drugs. By substituting gabapentin with pregabalin in postherpetic neuralgia therapy, we can compare the two drugs. Methods. Herpes zoster or shingles is a potential complication arising from the reactivation of dormant varicella zoster virus in dorsal root ganglion. 1 This reactivation causes a severe painful rash that spreads along dermatomes in the face or chest wall, which leads to postherpetic neuralgia (PHN). 1 In most cases, PHN occurs in older patients and persists even after the rash has cleared. 1 The pain Nonetheless, because standard pregabalin doses are more potent than standard gabapentin doses for similar medical conditions like postherpetic neuralgia (e.g. pregabalin 300 mg/day vs. gabapentin 900 mg/day – making the former dose approximately double as potent as the latter), it’s reasonable to expect that pregabalin users might Gabapentin is indicated as adjunct therapy for partial seizures and postherpetic neuralgia. 4 Pregabalin is indicated for the same uses as gabapentin, plus the management of fibromyalgia and neuropathic pain associated with diabetes, specifically diabetic neuropathy. 5 Pregabalin appears to have a better overall therapeutic effect than gabapentin for patients with PHN, but gabapentin has a lower incidence of adverse reactions and a better safety profile. Because both gabapentin and pregabalin must be titrated to an effective dosage and continued for an adequate duration to alleviate the pain associated with PHN, we were interested to determine how many patients with PHN receive effective dosages of these therapies and how long they continue them in real-world practice. For example, a recent cost analysis of adding pregabalin or gabapentin to the management of community – based patients with peripheral NeP, which estimated also the indirect costs, showed that although the pharmaceutical costs of pregabalin were significant, the overall patient cost was lower in the pregabalin group due to reduced sick leave Pregabalin showed superior results compared to gabapentin in the Visual Analog Scale (VAS) at various time intervals up to 12–14 weeks (SMD −0.47, 95% CI −0.74 to −0.19). Gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica) are both antiepileptic medications used to treat nerve pain and seizures, but they have some differences. Gabapentin is available as a lower-cost generic and is typically taken three times a day, while pregabalin is also available as a generic but is usually taken two or three times a day. Pregabalin appears to have a better overall therapeutic effect than gabapentin for patients with PHN, but gabapentin has a lower incidence of adverse reactions and a better safety profile. Clinicians should comprehensively consider patient factors and fully evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of each treatment option to select the most Gabapentin and pregabalin are FDA-approved to treat some of the same conditions, including postherpetic neuralgia in adults. Both drugs are also indicated to treat partial seizures in adults and certain children with epilepsy (a seizure disorder) when taken along with other medication. Background and objectives: There are limited data examining the real-world use of gabapentin and pregabalin for the treatment of post-herpetic neuralgia (PHN). ). This study examines dosing patterns, therapy outcomes, healthcare utilization and costs of patients with PHN who initiate treatment with gabapentin or prega
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |