Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |
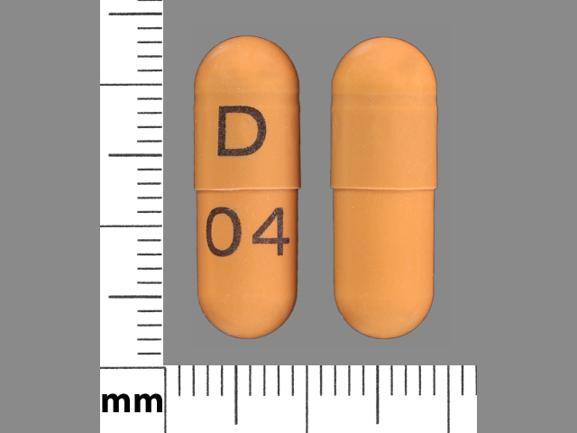
Gabapentin oral solution. The oral solution contains 250 millgrams of gabapentin per 5 milliliter (50 mg per mL) Neurontin or generic gabapentin. Gabapentin capsules. It’s available as 100-, 300- or 400-milligram gelatin capsules (Neurontin or generic gabapentin). Gabapentin enacarbil, 300- and 600-milligram extended-release tablets (Horizant). While a 200 mg gabapentin pill isn’t available, the medication does come in various other forms and dosages. The most common forms are capsules, tablets, and liquid solutions. Capsules are typically available in 100 mg, 300 mg, and 400 mg strengths. Tablets usually come in higher strengths of 600 mg and 800 mg. Liquid formulations often When taken as prescribed for an intended medical condition, gabapentin is well-tolerated and not considered addictive. However, addiction can occur or worsen when misused illicitly, at higher doses, or combined with opioids. Gabapentin has been increasingly associated with drug abuse, particularly in people who mix it with opioids, alcohol or other substances. Illegal diversion of gabapentin has led to its illicit availability on the streets, as well. Using gabapentin with opioids can be dangerous. Given its neurological effects, gabapentin has found a niche in some addiction treatment protocols. Notably, it is not a frontline treatment for opioid or alcohol use disorders, but clinicians sometimes use it off-label for certain symptoms or co-occurring conditions. Gabapentin’s relatively low risk of addiction compared to some traditional sleep medications has made it an attractive option for both patients and healthcare providers. However, it is crucial to understand the nuances of gabapentin’s use, benefits, and potential risks when considering it as a sleep aid. Gabapentin is available as Gralise, Neurontin, and generic gabapentin in the following dosage forms that are taken by mouth. 100 mg, 300 mg, 400 mg oral capsules 250 mg/5 mL oral solution Gabapentin may cause side effects such as dizziness, drowsiness, and dizziness. It is important to follow the prescribed dosage and seek medical attention if experiencing serious side effects or changes in mood or behavior. Gabapentin is prescribed by healthcare professionals and should only be taken under medical supervision. I brought her to the vet for a check up because she has a weird thing with drinking water constantly. They wanted to do blood work, but couldn’t because she wasn’t having it. So they rescheduled and gave me a drug called gabapentin, at 200 mg, to give her two hours prior to the appointment. According to reputable sources such as the Mayo Clinic, gabapentin is not considered addictive. It is a medication that is primarily used to manage seizures and treat nerve pain. However, it is essential to note that a small number of studies have reported misuse and abuse of gabapentin [2]. In addition its potentially addictive nature, gabapentin can cause suicidal thoughts, moods swings, and abrupt changes in a user’s behavior. It can also cause elevated blood pressure, fever, sleep problems, appetite changes, and chest pain. A Cochrane review reported that 3 to 4 patients out of every 10 with either of these conditions experienced at least a 50% reduction in pain intensity when prescribed gabapentin at dosages of 1800mg-3600 mg/day (gabapentin encarbil: 1200mg-3600 mg/day). This compared with only 1 or 2 out of every 10 given a placebo (an inactive treatment). · Oral capsule: 100 mg, 300 mg, 400 mg · Oral tablet: 600 mg, 800 mg · Oral solution: 50 milligrams per milliliter (mg/mL) Gralise: Gabapentin · Oral tablet: 300 mg, 600 mg: Horizant: Gabapentin enacarbil · ER tablet: 300 mg, 600 mg: Lyrica: Pregabalin · Oral capsule: 25 mg, 50 mg, 75 mg, 100 mg, 150 mg, 200 mg, 225 mg, 300 mg · Oral Is 200 mg of gabapentin addictive? While gabapentin is not considered as addictive as opioids, there is still a potential for abuse and dependence , especially with long term and higher doses. Misusing gabapentin by taking higher doses can lead to adverse effects and dependence. Some people also use gabapentin recreationally, which can lead to the potential for addiction or abuse. Is Gabapentin Addictive? Yes. Though it’s recognized as a controlled substance in only a few states and is less addictive than opioids, gabapentin misuse can still lead to addiction and withdrawal symptoms. Gabapentin is not likely to cause addiction, but it may lead to dependence or misuse under certain conditions. As such, doctors prescribe gabapentin carefully to avoid withdrawal Adults and children 12 years of age and older—At first, 300 milligrams (mg) 3 times per day. Your doctor may adjust your dose as needed and tolerated. However, the dose is usually not more than 1800 mg per day (600 mg 3 times per day). Children 3 to 11 years of age—Dose is based on body weight and must be determined by your doctor. Is Gabapentin Addictive? While Gabapentin is not classified as a controlled substance in the U.S., it has the potential for abuse and dependence. People who misuse gabapentin often develop tolerance, requiring higher doses to achieve the same effects, and ]experience withdrawal symptoms if they stop using it. Some individuals may mistakenly assume that gabapentin is not habit-forming or addictive. While gabapentin is not considered to have a high potential for addiction compared to other substances, cases of gabapentin misuse, abuse, and addiction have been reported. Total Daily Dose (mg) Directions: 1-3: 2400 mg: Take 1200 mg by mouth twice daily for 3 days. 4-6: 1800 mg: Take 900 mg by mouth twice daily for 3 days. 7-9: 1200 mg: Take 600 mg by mouth twice daily for 3 days. 10-12: 800 mg: Take 400 mg by mouth twice daily for 3 days. 13-15: 400 mg: Take 200 mg by mouth twice daily for 3 days. 16-18: 200 mg
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |