Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
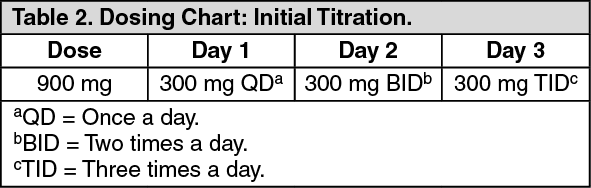
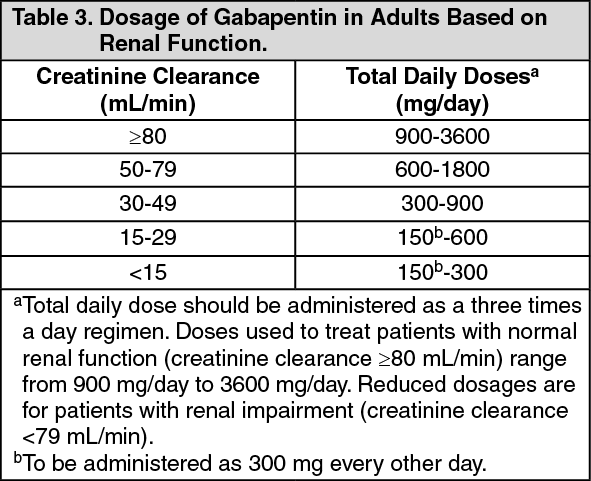
There are several studies of gabapentin in children with partial seizures. In 1996, Khurana and colleagues reported the results of an open-label add-on trial in 32 children (ages 2-16 years) with refractory partial seizures.4 The children were treated with gabapentin doses of 10 to 50 mg/kg/day, with an average effective dose of 26.7 mg/kg/day. The recommended maintenance dose of NEURONTIN in patients 5 to 11 years of age is 25 mg/kg/day to 35 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. NEURONTIN may be administered as the oral solution, capsule, or tablet, or using combinations of these formulations. Dosages up to 50 mg/kg/day have been well tolerated in a long-term clinical study. If your child is sick less than 30 minutes after having a dose of Gabapentin, give them the same dose again. If your child is sick more than 30 minutes after having a dose of Gabapentin, do not give them another dose. Wait until the next normal dose. If your child is sick again, seek advice from your family doctor, nurse, pharmacist, or hospital. Initially 200-500 micrograms/kg (max 10mg per dose) nocte. Maximum 1mg/kg BD (Max daily dose 75mg) Child 12-17 years nocte. Higher doses (> 750 micrograms/kg) or doses up to 150mg a day can be given under specialist advice Carbamazepine (licensed) Typically for trigeminal neuralgia Dose as per BNFc Gabapentin (off-label) 1 The recommended maintenance dose of NEURONTIN in patients 5 to 11 years of age is 25 mg/kg/day to 35 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. NEURONTIN may be administered as the oral solution, capsule, or tablet, or using combinations of these formulations. Dosages up to 50 mg/kg/day have been well tolerated in a long-term clinical study. There was a statistical improvement in weight-for-age Z scores from 24 hours prior to gabapentin initiation to 2 weeks after the maximum dose of gabapentin (−2.23 ± 1.78 to −1.66 ± 1.91, p < 0.001) and a reduction in FLACC scores (2.29 ± 1.64 to 1.52 ± 1.76, p = 0.007) from 24 hours prior to gabapentin initiation to 3 days after the Medical information for Gabapentin on Pediatric Oncall including Mechanism, Indication, Contraindications, Dosing, Adverse Effect, Interaction, Renal Dose, Hepatic NEURONTIN is indicated for the treatment of partial seizures with or without secondarily generalised tonic-clonic seizures, in adults and children age 3 years and above who have not achieved adequate control with standard anti-epileptic drugs (see section 4.2 Dose and method of administration). Used to treat restless legs syndrome in adults and occasionally in children/adolescents. Gradual dose increase helps to minimize sedation. May need to adjust dose in renal impairment. Space doses at least 2 hours from antacids (decreases absorption of gabapentin). Adverse effects: somnolence, ataxia, fatigue, and depression. Used to treat restless legs syndrome in adults and occasionally in children/adolescents. Space doses at least 2 hours from antacids (decreases absorption of gabapentin). Adverse effects: somnolence, ataxia, fatigue, and depression. Starting doses of Gabapentin may be 5 mg/kg oral once a day at night-time, to be increased to twice daily the next day and then three times a day on the third day. In adolescents, typical starting doses are 300 mg orally, following the same schedule of increasing frequency on the first 3 days of use. After surgery, patients received standardized patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) and continued on gabapentin 5 mg/kg or placebo every 8 hours for 5 days. The primary endpoints were opioid consumption, pain scores, and the presence of opioid adverse effects. morphine PCA and acetaminophen. Administer NEURONTIN three times a day using 300 mg or 400 mg capsules, or 600 mg or 800 mg tablets. The maximum time between doses should not exceed 12 hours. The starting dose range is 10 mg/kg/day to 15 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses, and the recommended maintenance dose reached by upward titration over a period of approximately 3 days. These pharmacokinetic data indicate that the effective daily dose in pediatric patients with epilepsy ages 3 and 4 years should be 40 mg/kg/day to achieve average plasma concentrations Medscape - Seizure dosing for Neurontin, Gralise (gabapentin), frequency-based adverse effects, comprehensive interactions, contraindications, pregnancy & lactation schedules, and cost Equianalgesic dose refers to the amount of opioid equivalent to 10mg IV morphine. To convert between opioids determine the morphine equivalent of the first drug. Then convert the morphine equivalent dose to the new drug utilizing the table. Child 6–11 years 10 mg/kg once daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 1, then 10 mg/kg twice daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 2, then 10 mg/kg 3 times a day (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 3; usual dose 25–35 mg/kg daily in 3 divided doses, some children may not tolerate daily increments; longer intervals (up to weekly) may be more appropriate, daily dose maximum to be given in 3 divided Detailed Gabapentin dosage information for adults and children. Includes dosages for Restless Legs Syndrome, Epilepsy and Postherpetic Neuralgia; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments. Pediatric Patients Age 3 to 11 years. The starting dose range is 10 mg/kg/day to 15 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses, and the recommended maintenance dose reached by upward titration over a period of approximately 3 days. The recommended maintenance dose of NEURONTIN in patients 3 to 4 years of age is 40 mg/kg/day, given in three divided The recommended maintenance dose of NEURONTIN in patients 5 to 11 years of age is 25 mg/kg/day to 35 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. NEURONTIN may be administered as the oral solution, capsule, or tablet, or using combinations of these formulations. Dosages up to 50 mg/kg/day have been well tolerated in a long-term clinical study.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |