Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 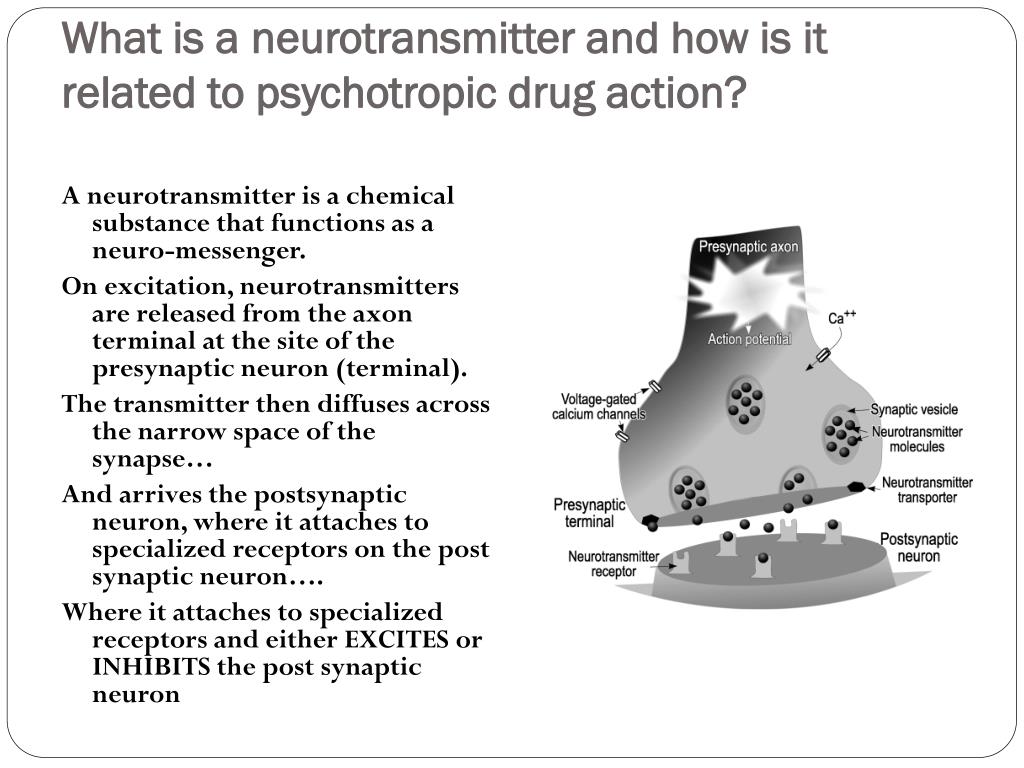 |
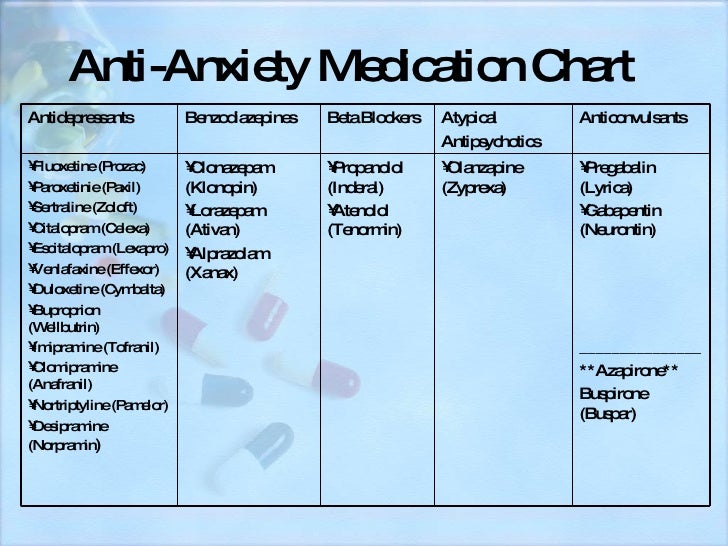
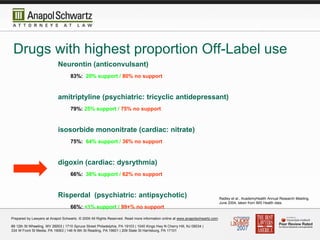
tain medications nonformulary or, in some cases, sim-ply unavailable.24 Concerns regarding misuse of medications, includ-ingpsychiatricmedications,oftenshapedrugformular-ies in correctional settings. Individuals may misuse medications, even noncontrolled medications, for se-dating, hypnotic, stimulating, or toxic effects, among Neurontin is an anti-epileptic drug, also called an anticonvulsant. It affects chemicals and nerves in the body that are involved in the cause of seizures and some types of pain. Neurontin is used in adults to treat neuropathic pain (nerve pain) caused by herpes virus or shingles (herpes zoster). Gabapentin is a nerve pain medication and anticonvulsant that has proven to be effective for people who have hard-to-treat depression or other mood disorders. Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) is a medicine used to treat partial seizures, nerve pain from shingles and restless leg syndrome. It works on the chemical messengers in your brain and nerves. Antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) are psychotropic agents; that is, they act on the mind and can positively or negatively influence behavior. This result is expected, given their mechanisms of action, which are to alter ion channel and neurotransmitter system functions and, thereby, modulate the electrochemical systems that underlie behavior. Gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica) are both gabapentinoids—psychotropic medications that cross the blood-brain barrier and mimic the inhibitory neurotransmitter Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Gabapentin was first approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 as an adjunctive treatment for partial seizures. In 2002 Gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica) are both gabapentinoids—psychotropic medications that cross the blood-brain barrier and mimic the inhibitory neurotransmitter Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Many psychotropic medications may be listed under various classifications and may be used for treatment of several psychiatric illnesses. For example, some medications listed under antipsychotics maybe used as a mood stabilizer. The Executive Formulary Committee does not endorse the use of nonformulary drugs. Texas HHS Psychiatric drug formulary Forms listed with a "Blank" medication name are the base form available in English and Spanish versions. Complete a blank form if no prefilled version exists for the prescribed psychotropic medication. The Client Rights Office accepts questions about these forms and suggestions for improvements. “Psychotropic medication” means a prescription drug, as given in s. 450.01 (20), Stats., that is used to treat or manage a psychiatric symptom or challenging behavior. For training purposes, below is a list of psychotropic medications or medications with psychotropic uses. Gabapentin is commonly used off-label in the treatment of psychiatric disorders with success, failure, and controversy. A systematic review of the literature was performed to elucidate the evidence for clinical benefit of gabapentin in psychiatric disorders. There is sufficient evidence to consider gabapentin as a third-line treatment for social anxiety disorder and severe panic disorder. Gabapentin (Trade name: Neurontin) is an anticonvulsant. It is commonly also used off-label for anxiety disorders, restless leg syndrome, and in alcohol use disorder. It is structurally similar to GABA but does not directly bind to GABA receptors. medication’s efficacy for such use does exist however. This type of medication use is referred to as "off label." Remember, always consult your doctor or pharmacist with any specific medication questions Generic Name Brand Name Current Uses alprazolam Xanax anxiety, panic amitriptyline Elavil, Endep depression (tricyclic) The author erroneously stated: “Gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica) are both gabapentinoids—psychotropic medications that cross the blood-brain barrier and mimic the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA).” 1 Gabapentin, a medication that sounds like it could be the name of a quirky robot sidekick in a sci-fi flick, is actually a serious player in the world of pain management and neurological disorders. Originally developed to treat epilepsy, this versatile drug has found its way into the treatment plans for conditions ranging from neuropathic pain Gabapentin has less likely benefit adjunctively for bipolar disorder. Gabapentin has clearer efficacy for alcohol craving and withdrawal symptoms and may have a role in adjunctive treatment of opioid dependence. There is no clear evidence for gabapentin therapy in depression, PTSD prevention, OCD, or other types of substance abuse. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant that is eliminated by the kidneys and is not protein bound. 8 By virtue of these properties as well as lack of hepatic enzyme induction, gabapentin has little potential for drug interactions with psychotropic medications, 8 which is of great importance in treating a complicated psychiatric disorder such as PTSD. Gabapentin’s potential for stabilizing mood and easing discomfort makes it a versatile tool for treating mental health issues. Here’s what you need to know: Gabapentin’s action mechanism makes it a favorable medication for treating various types of mental disorders. Gabapentin’s benefits include symptom relief and safety. Neurontin – an anticonvulsant which is sometimes used as a mood stabilizer, anti-anxiety agent or to treat chronic pain, particularly diabetic neuropathy; Norapramin (desipramine) – an antidepressant, also used in the treatment of nerve pain
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |